
Lignovations at Royal Society of Chemistry Emerging Tech 2023
Juli 18, 2023
Lignovations at IFSCC Sustainability Challenge
August 22, 2023written by Stefan Beisl, PhD
Lignin is a complex and heterogeneous biopolymer present in the cell walls of plants where it provides strength, rigidity, and resistance to degradation of the plant tissue. As the natural protectant of plants, lignin comes with valuable properties that can be used in a wide variety of industrial applications. However, its heterogeneity makes it challenging to work with. In this blogpost we share the sources of lignin’s heterogeneity and how we solve it at Lignovations.
All lignins are not Created Equal: Sources of Lignin Heterogeneity
There are three major sources of heterogeneity that influence the quality, structure, and functional properties of lignin:
1. The species and origin of a plant
The species and origin of a plant affect the molecular structure and monomer composition of its lignin. Even two plants of the same species and origin that were exposed to different environmental influences during their growth develop differing lignins.
2. The lignin extraction or separation method
The lignin extraction or separation method requires breaking the covalent bonds between lignin and hemicelluloses and depolymerizing lignin to some extent. Multiple different separation methods for lignocellulosic biomass are used by the pulp and paper industry as well as modern biorefineries. These fundamentally different separation methods have led to the commercial availability of lignins with strongly different characteristics. Lignins from a kraft process compared to lignins from a combination of mild thermomechanical pretreatment and enzymatic hydrolysis can be seen as the uttermost qualities commercially available today. The lignin out of a kraft process shows very severe changes of its native molecular structure, including incorporation of sulfur, while the enzymatic hydrolysis process only solubilizes the carbohydrates bound to the lignin leading to a much more native structure in the extracted lignin.
3. The inherent heterogeneity of lignin’s molecular structure
Even two samples of lignin that were extracted with the same process from the same plant will feature important differences. This inherent heterogeneity of lignin’s molecular structure results mainly from the following influencing factors:
In practice, this heterogeneity leads to inconsistent processing characteristics, limited compatibility, unpredictable properties, and uncertain reactivity. As a result, comparability and reproducibility is difficult to achieve, which often leads to inconsistent theories and results in the scientific community and during commercial product development which makes the use of lignin in industrial applications or consumer products almost impossible. Therefore, overcoming lignin’s heterogeneity is key for industrial applications.
Solving lignin’s heterogeneity for industrial use
Today, established biomass fractionation facilities prioritize carbohydrate valorization and therefore do not focus on reducing lignin’s heterogenity for high-value applications. Consequently, for commercially available lignins today, heterogeneity can only be tackled after it has been extracted. The two most relevant methods are the (1) depolymerization of the lignin and (2) the modification of its molecular structure. This is done via chemical or enzymatical pathways. Both approaches include precise chemical reactions and/or cleavage of bondings which can be executed well on a homogeneous molecule but are again hindered by the heterogeneity of lignin. Therefore, it is difficult to create a robust process based on these technologies.
Therefore, we have turned to a completely different approach that is based on physical rather than chemical processing.
How Lignovations Solves the Problem of Lignin Heterogeneity
Lignovations combines two approaches to solve the problem of lignin heterogeneity without the use of chemical reactions:
1. Our fractionation technology separates lignin into different fractions based on their solubility in various solvents or solvent mixtures. This allows for obtaining lignin fractions with narrow molecular weight distribution, high purity, and selected functionalities. In our manufacturing process, we use the dependency of the lignin solubility in green organic solvent/water systems (Figure 1). We achieve the fractionation by adjusting the ratio of solvent to water in the system. As a result making our process robust to the varying properties of lignin from different sources and extraction processes.

Figure 1. Representation of a typical solubility behavior of lignin in a water/organic solvent system
2. Our precipitation technology makes use of the physical alignment of lignin molecules to reduce the inherent heterogeneity of the lignin molecule. In a very simplified perception, the lignin molecule has areas in which it is relatively hydrophobic, and other areas, in which it is rather hydrophilic. During the precipitation process, water is added in a specific way to induce the orientation of hydrophilic areas of the lignin molecules on the particle surface (Figure 2).
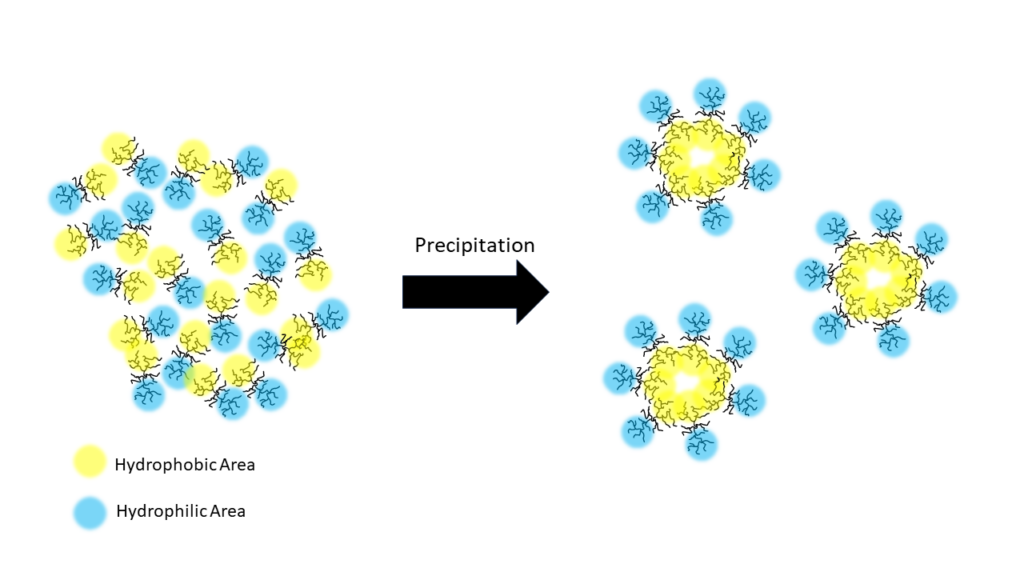
Figure 2. Simplified representation of the physical alignment during the precipitation and the resulting homogenous surface of the particles
By combining these two approaches, Lignovations produces lignin particles with uniform size, shape, and surface properties in consistent quality. Hence, enabling the use of lignin’s natural functions in high-value applications.
The improved homogeneity of the particle surface compared to the untreated lignin significantly reduces the problems caused by the natural heterogeneity of lignin. This structure enhances the dispersibility and compatibility of lignin particles with other materials. Furthermore, these particles can serve as a good template for further surface modifications and compatibilizations. These can expand the range of applications for lignin even more. For example, lignin particles can be functionalized with different groups to improve their adhesion, stability, or reactivity.
Let’s Unlock Lignin’s Possibilities Together
We are always looking for potential collaboration partners to make use of lignin and develop exciting applications. Contact us to learn more about our unique lignin or to explore collaboration opportunities.





